Salmon is a well-known fish that’s an excellent source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids and various vitamins and minerals. An extensive list of health benefits accompanies this nutrient-rich fish — as do plenty of reasons why you should add more of it to your diet.
Regularly consuming salmon has been shown to improve our cardiovascular health, support brain function, protect our neurological systems, promote bone and joint health, boost our metabolisms and impart anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects on our bodies. This means that adding salmon to your regular diet can promote your lifelong health and development. Read more below about the nutrients found in salmon and how they can impact your health.
Salmon Is Rich in Protein
Salmon is very high in protein and contains all nine essential amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) that the human body requires for proper growth and maintenance. The proteins in salmon are easier for your body to digest and absorb compared to other protein sources. These proteins are known to promote weight loss by boosting your metabolism and helping you feel fuller longer. Just a small 4-ounce serving of salmon contains over half of your daily required protein intake.

Salmon Is a Prime Source of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Perhaps the most famous nutrient this oily fish is known for is its high content of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Omega-3s are essential unsaturated fatty acids that your body can’t spontaneously create on its own and that are vital for normal metabolism and various bodily functions. Studies have shown that omega-3s have a variety of health benefits, such as the following:

- Reduced cancer risks: Studies have suggested that the intake of omega-3 fatty acids may slow tumor growth and improve quality of life in cancer patients. Doctors may also suggest a diet high in omega-3s as a preventative measure against cancer.
- Protection of the cardiovascular system: Consumption of fatty fish high in omega-3 fatty acids has been linked to decreased risk of cardiovascular problems, such as heart attacks, strokes, arrhythmias and high blood pressure. It also decreases blood cholesterol levels. Salmon is often recommended as a part of a heart-healthy diet.
- Improved cognition and better moods: The high amounts of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, found in salmon are vital in supporting the brain and neurological system. Studies have shown that omega-3s can decrease the risk of depression and slow the progression of psychological disorders, such as schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. High amounts of DHA are also required during pregnancy for proper fetal brain development, and omega-3s can also limit ADHD in children.
- Better vision: Omega-3 fatty acids are required for healthy eye development and maintenance, and consumption of them can help prevent chronic dry eyes. These fatty acids also play a role in the prevention of macular degeneration, which is the main cause of age-related vision loss.
- Reduced inflammation: Omega-3 fatty acids are known to have strong anti-inflammatory properties and can reduce inflammation in the cardiovascular and digestive systems. These anti-inflammatory properties also reduce the risk of cancer and autoimmune diseases and can exert anti-aging effects for healthy skin.
- Improved bone and joint health: Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids can reduce bone resorption and limit inflammatory joint conditions such as osteoarthritis.
Ample Vitamins and Minerals Are Present in Salmon
Other vitamins and minerals found in salmon include the following:

- Calcium: This mineral is essential for bone health, and salmon happens to contain high concentrations of it. Calcium is also important for a healthy heart, muscles and nervous system and for hormone secretion.
- Vitamin D: Salmon is a reputable source of this vitamin, which is vital for the absorption of calcium for proper bone formation, growth and maintenance. It also boosts your immune system and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Potassium: This important electrolyte is required for proper cardiovascular, muscular and neurological functioning. It can also help lower cholesterol and blood pressure and prevent excessive fluid retention.
- Vitamin A: Typically associated with carrots, this nutrient is partially responsible for giving salmon its pinkish-red color. Vitamin A is known to maintain healthy vision and bones, and its derivative, retinol, is famous for promoting healthy hair, skin and nails.
- Selenium: Known as an effective antioxidant, this mineral can help prevent cancer by neutralizing free radicals in your body. It also helps maintain your immune system and insulin levels. Selenium even promotes normal brain and thyroid function.
- Riboflavin: Also known as vitamin B2, this nutrient can help reduce inflammation and metabolize fats, carbohydrates and proteins.
- Niacin: Also known as vitamin B3, niacin is a powerful antioxidant that can help lower your cholesterol levels.
- Pantothenic acid: Also known as vitamin B5, this nutrient is important in synthesizing and metabolizing proteins, carbohydrates and fats. It’s known to improve heart health, boost immunity, alleviate stress and improve respiratory and skin disorders, among other things.
- Vitamin B6: This vitamin supports healthy brain functioning and your metabolism.
- Biotin: Also known as vitamin B7, biotin aids metabolism and tissue maintenance. It also has protective effects on your cardiovascular and neurological systems.
- Vitamin B12: Also known as cobalamin, this nutrient plays a vital role in the functioning of your brain and nervous system. It’s important in the formation of red blood cells.
- Vitamin E: This famous antioxidant is important for regulating metabolic processes, strengthening your immune system and keeping your skin smooth and supple.
- Magnesium: This super mineral has multiple supportive functions, including maintaining a healthy neurological system, cardiovascular system, metabolism and strong bones. It can also reduce inflammation and help prevent diabetes by regulating blood sugar levels.
- Phosphorus: Not only does this mineral help synthesize protein for the maintenance of cells and tissues, but it also plays a role in the formation of bones and teeth.
Here’s What to Look For When Buying Salmon
To ensure you’re purchasing the freshest cuts of salmon, be sure to look for the following:
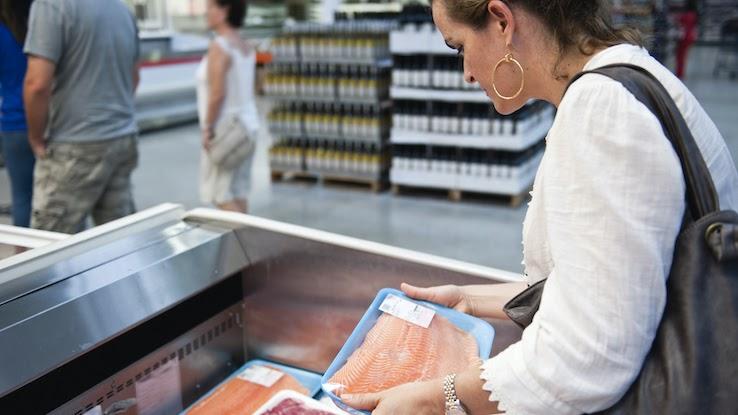

- A deep pinkish color with smooth, clean cuts if in the steak or fillet form
- Firm, elastic flesh that’s translucent
- Airtight packaging with no liquid
- Mild aroma
- If purchasing a whole fish, firm, glossy skin with bright red gills and clear eyes that aren’t cloudy
Generally, most of the Atlantic salmon available at your local grocery store today are farmed, whereas Pacific salmon are typically wild caught. There have been numerous debates over the pros and cons of eating wild or farmed salmon due to sustainability issues and mercury toxicity levels, but there’s no definite answer as to which is healthier.
The Journal of the American Medical Association suggests that the benefits of eating salmon outweigh the risk of the contaminants. Because the rules and regulations in regard to fish farming and catching have progressively become more sustainable, cost-effective and rigorous, both wild-caught and farmed salmon available today are safe for consumption.
Resource Links:
https://www.organicfacts.net/salmon.html
https://globalsalmoninitiative.org/en/about-salmon-farming/nutrition/
https://www.livestrong.com/article/117686-health-benefits-salmon/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminA-HealthProfessional/
https://www.livescience.com/51966-vitamin-b2-riboflavin.html
https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-niacin/art-20364984
https://www.livescience.com/51640-b5-pantothenic-acid.html
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-HealthProfessional/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-vitamin-b12/art-20363663
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminE-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Phosphorus-HealthProfessional/
https://www.cooksillustrated.com/articles/641-how-to-buy-prep-and-cook-salmon
https://www.epicurious.com/ingredients/how-to-buy-salmon-at-the-grocery-store-article