Without a doubt, indoor painting is a common home improvement project. After all, there’s no easier way to completely transform a space. However, that splash of color may not be completely risk-free. That is, with proper ventilation, and in the right conditions, painting can be a perfectly safe activity, but if you aren’t careful — or if you’re working in an environment with poor ventilation — the use of paints that give off dangerous fumes can lead to harmful health effects.
Types of Paint
Latex:

Latex paint is commonly used for indoor projects because it can be easily cleaned and dries relatively quickly. However, it can cause stomach discomfort or vomiting if ingested, even though it is not poisonous.
Oil-based:
Oil-based paints are irritating to the skin. If ingested, oil-based paints pose a greater risk than latex paints. If oil-based paint is aspirated (inhaled) during choking, it can lead to pneumonia in the lungs.
Solvent-based:
Solvent-based paints can cause skin irritation as well. Additionally, they give off fumes that, when inhaled, can lead to dangerous symptoms.
What Makes Paint Fumes Dangerous?
VOCs, or volatile organic compounds, are a byproduct of either solids, liquids or a combination of both in paint. When paint is applied, the byproduct is released into the atmosphere in the form of a gas (paint fumes). VOCs are generally present at a higher concentration when painting indoors — in fact, as much as 10 times higher than when painting outdoors.

The term VOC refers to a variety of different chemicals, many of which can have a negative effect on a person’s health. In addition to paints, VOCs can also be found in many other products, including:
- Lacquers
- Varnishes
- Cleaning products
- Pesticides
- Office printers
- Carbonless copy paper
- Glues
- Adhesives
- Permanent markers
- Photocopiers
- Fuels
- Cosmetics
- Crafting materials
Negative Health Effects Caused By the VOCs in Paint Fumes
There is a wide variety of both short-term and long-term negative health effects associated with VOCs in paint fumes. The severity of the health effect depends on several different factors, including both the length of time and the level of exposure. Some examples of short-term, temporary side effects include:

- Irritation of the eyes, nose, throat or and/or respiratory tract
- Visual disturbance
- Headache
- Loss of coordination
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Allergic skin reaction
- Fatigue
- Memory impairment
Some of the conditions above can become chronic in individuals who are regularly exposed to VOCs in paint fumes either in the home or at work. Long-term health effects of VOCs may include:
- Liver damage
- Kidney damage
- Central nervous system damage
- Certain types of cancer
- Asthma
How Long Do VOCs Last?
The odor emitted from freshly dried paint is a result of the ingredients within the paint that make it a liquid substance. These substances evaporate into the air while the wet paint is drying. The wetter the paint, the more substances are released into the air and the stronger the odor. As the liquid portion of the paint continues to evaporate, odorous paint fumes continue to form. As evaporation proceeds, the process of dispersion also occurs.

Dispersion occurs when the fumes mix with the air and are dispersed into the environment. As dispersion occurs, more and more of the fumes are carried throughout the air, which makes them less concentrated, and the odor less strong. When the paint is dried entirely and the fumes are completely dispersed, the odor eventually disappears. Remember: VOCs are at their highest concentration when paint is freshly wet.
Paint Fumes and Pregnancy
Many healthcare professionals recommend that pregnant people avoid exposure to paint so as to avoid potential fumes. Exposure to VOCs in paint is believed to be associated with an increased risk of miscarriage. Additionally, babies and young children should not be exposed to wet paint as they are more susceptible to damage from its effects.

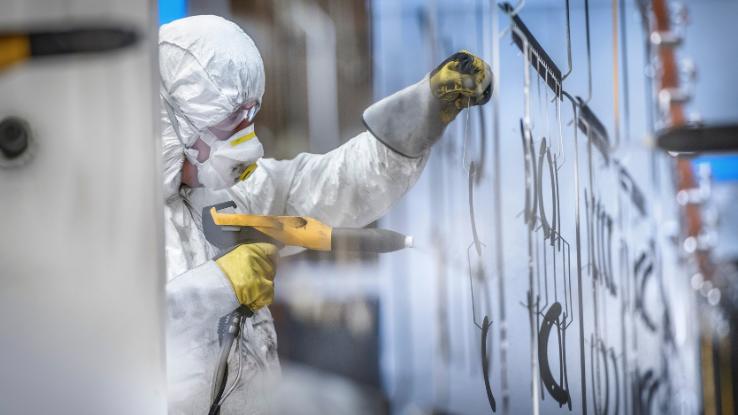
How to Protect Yourself
When painting or using other substances that may contain VOCs, it is recommended that one use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes gloves, which helps one avoid direct contact with paint, and a mask that contains a filter, which reduces the number of harmful particles one is inhaling.

In addition, use of these substances is not recommended in enclosed spaces, where there is inadequate ventilation. Try to paint outdoors when possible. If you think you have been exposed to paint fumes and are feeling any of the aforementioned symptoms, it is important to contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Resource Links: