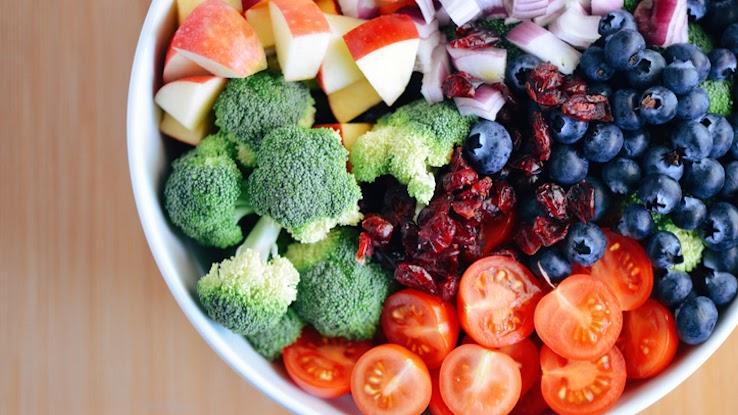
In recent years, antioxidants have been frequently discussed for their ability to improve people’s health by protecting against free radicals — unstable molecules that can hurt the cells throughout your body. The harmful effects of free radicals include the damage they can do to cell membranes and your DNA, contributing to cancer and other diseases. Free radicals are found everywhere, including in the environment and certain foods, such as fried ones.
Eating foods rich in antioxidants may combat free radicals and make them harmless by breaking down their molecular structure. There are dozens of different forms of antioxidants. Some of the most common antioxidants found in foods include vitamins A, C and E, along with selenium, beta carotene and lutein. Incorporating more foods into your diet that are rich in antioxidants is beneficial to your overall health — and the changes are easy to make. Below are 10 antioxidant-rich foods to get you started.
Sweet Potatoes
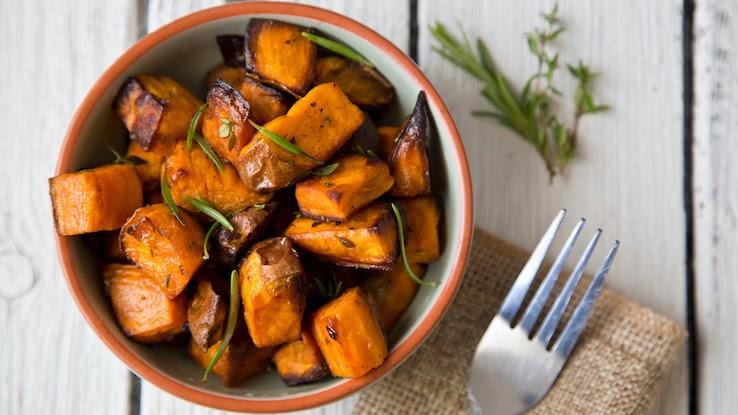

Sweet potatoes are high in the antioxidants beta carotene and vitamin E. Beta carotene is beneficial to your body in a few ways, such as assisting your reproductive system and immune system in functioning correctly. Vitamin E may help to keep red blood cells healthy. Consider eating more sweet potatoes by switching out regular French fries with homemade baked sweet potatoes.
Kale
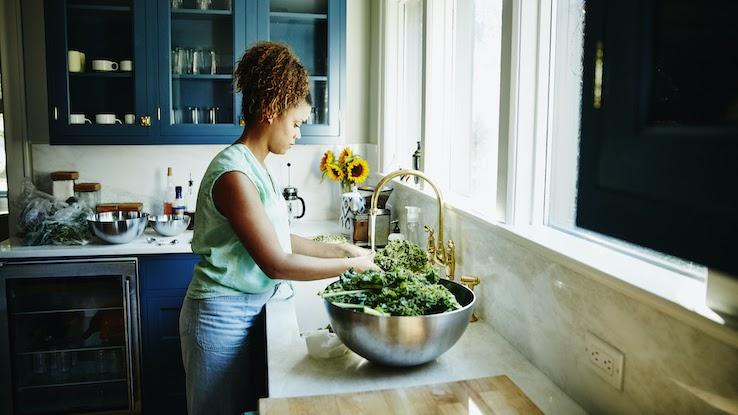

Kale may not be a vegetable everyone is familiar with. Still, it’s a perfect choice if you want to increase the antioxidant-rich foods in your diet. Kale contains several flavonoids, beta carotene and lutein. Together these various antioxidants help prevent inflammation in your body. Incorporating kale into your diet is as easy as adding a few leaves on top of your sandwich or burger or putting some kale into your salad. Just remember to remove the tough center rib first.
Spinach
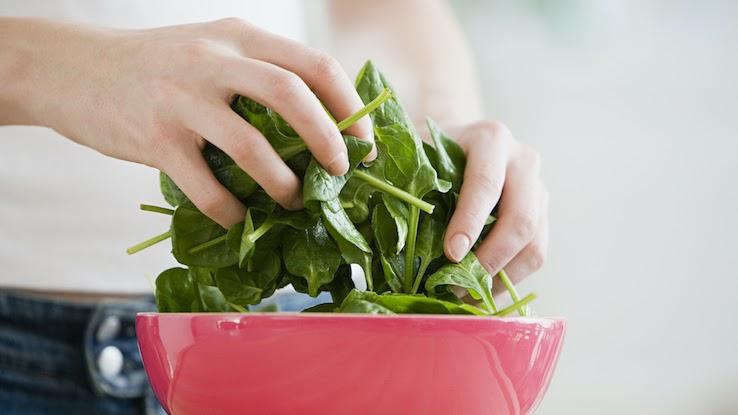

Another food high in beta carotene and vitamin E is spinach. Spinach also contains the antioxidant lutein, which is essential for maintaining good vision by preventing the formation of cataracts. It can also decrease the chances you’ll develop an eye condition called macular degeneration that’s a result of aging. Add fresh spinach to salads, omelets and sandwiches.
Tomatoes
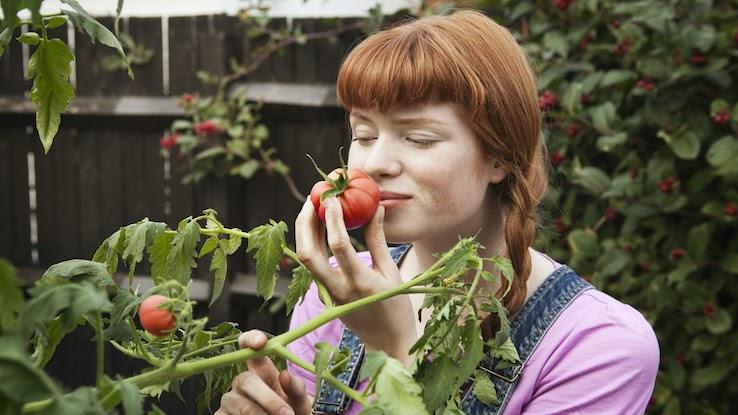

Tomatoes are a great choice when selecting foods that are rich in antioxidants. Along with vitamin C, vitamin E and beta carotene, tomatoes contain the antioxidant lycopene. According to several studies, lycopene is beneficial to the body in several ways, including lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease and certain types of cancer. Lycopene also plays a role in keeping bones healthy. Add a few tomatoes to your salad, slice them onto a sandwich or start dinner off with a nice homemade bruschetta.
Blueberries
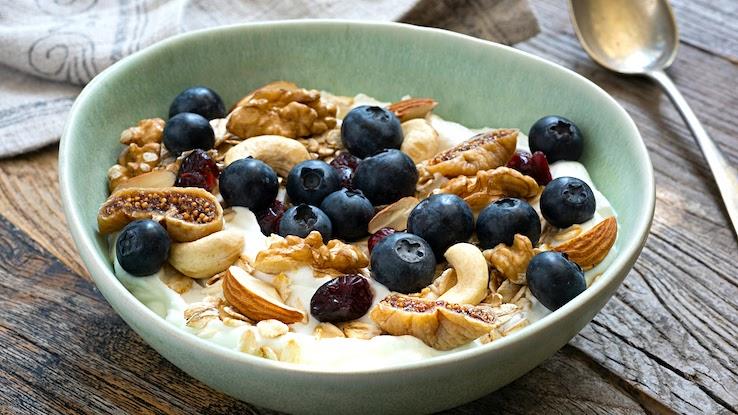

Blueberries are often at the top of nutritionists’ lists of antioxidant-rich foods, and for good reason. They contain the antioxidants beta carotene and lutein, along with vitamins A, C and E. If the antioxidant benefits of blueberries weren’t enough of a reason to add some to your diet, blueberries also contain fiber, folate and vitamin B complex. Incorporating blueberries into your diet is very easy: Just add them to your cereals and oatmeal or snack on a handful. They’re even great on summer salads.
Almonds
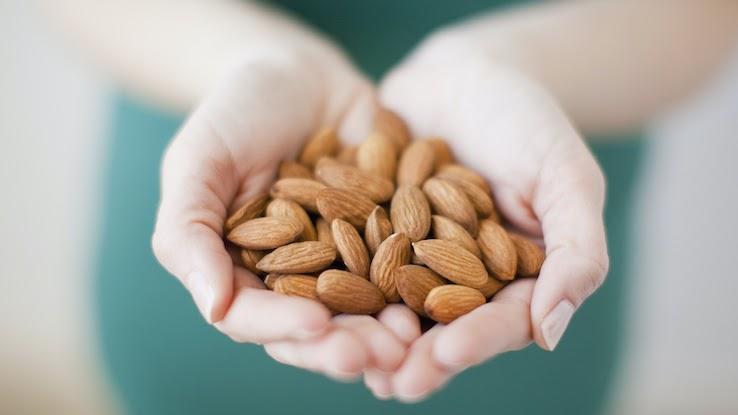

Almonds contain a type of antioxidant known as flavonoids, which protect your body from inflammation, help increase vitamin C effects and protect blood vessels in your body. Sprinkle a few in yogurt or oatmeal. In addition to the antioxidant benefits, almonds add protein and may help lower cholesterol. Almonds are the perfect snack between breakfast and lunch, too.
Wheat Germ
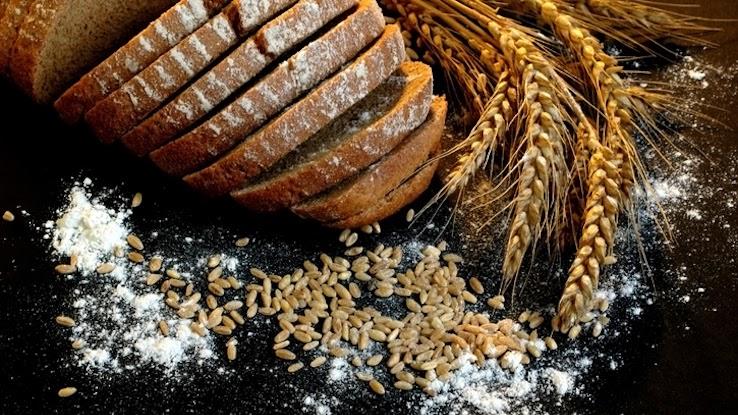

Wheat germ is a wheat kernel that contains several nutrients, including the antioxidants vitamin E and selenium. Both antioxidants help improve the functioning of your immune system. Selenium also helps to regulate your thyroid gland. Wheat germ is relatively easy to add to your diet. Put it on cereal or toast, or add it to protein shakes and smoothies.
Broccoli
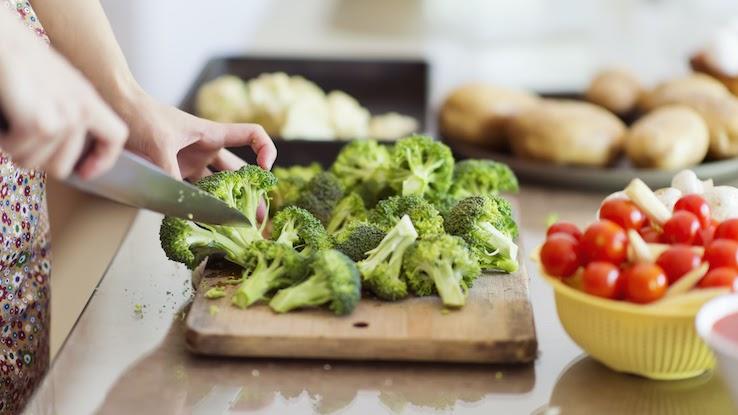

If your family ever told you to eat your broccoli when you were a kid, they were right. Broccoli contains several antioxidants, including vitamin C, vitamin E, lutein and beta carotene. In addition, it also contains the antioxidant kaempferol, which may help reduce low-density lipoprotein and lower cholesterol levels, according to the LSU Agricultural Center. Raw or steamed is the best way to eat broccoli to get the most antioxidant benefits.
Beans

According to several scientific studies, beans contain phytochemicals, which act as antioxidants and may play a role in preventing colon cancer. Beans also contain antioxidants, including selenium and vitamin C. Incorporate beans into your diet by tossing some into casseroles, soups, stir-fries and rice dishes.
Raisins
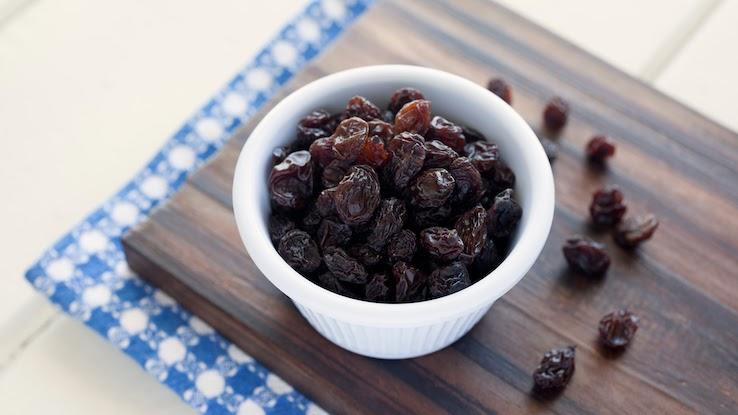

Raisins contain vitamin C, vitamin E and the antioxidant selenium. Raisins have triple the concentration of antioxidants compared to their counterpart, grapes. Add raisins to your diet by putting a handful in salads, cereal, rice or yogurt. Raisins are also low in fat and make a quick snack on the go.
According to the National Cancer Institute, more studies are needed to conclusively state antioxidants can prevent cancer, but they do provide other health benefits. One of the main benefits of antioxidants is their ability to protect your body from damage caused by free radicals. Other health benefits include keeping your immune system functioning correctly, maintaining bone health and decreasing inflammation in your body. With a bit of planning, it’s easy to add a few antioxidant-rich foods to your diet every day.
Resource Links:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2841576/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5745491/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5456284/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3902183/