What Is Cellulitis Disease? Symptoms, Medicines and Prevention

Cellulitis is a common bacterial infection that affects the deeper layers of your skin. It causes painful redness and swelling — and without treatment, it can spread and cause serious health problems. Learn about cellulitis symptoms, treatments and prevention steps.
What Are the Symptoms of Cellulitis?
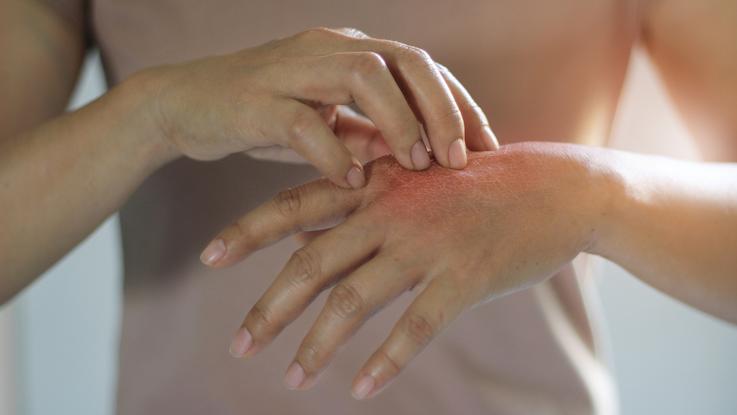
The most common symptom of cellulitis is red, swollen areas on the skin. These areas are usually painful and warm to the touch. Other symptoms include:
- Pitted or scaly areas on the skin
- Blisters
- Headache
- Fever
- Chills
Cellulitis most commonly affects the feet and legs, but it can happen anywhere on the body.
What Causes Cellulitis? Am I at Risk?

Various types of bacteria can cause cellulitis, but staph bacteria and group A strep bacteria are the most common causes. The bacteria often enter your body through skin abrasions or wounds, like after an injury or surgery. Cellulitis isn’t contagious — you can’t catch it from or spread it to other people.
Anyone can get cellulitis, but certain other health conditions put you at higher risk, including:
- Breaks in your skin like cuts, ulcers, puncture wounds, injection sites, bites, piercings or tattoos
- Chronic skin conditions like eczema, fungal infections or dermatitis
- Chickenpox and shingles
- Chronic health conditions like obesity or diabetes
- Chronic swelling in your limbs (like chronic edema or lymphedema)
- Problems with your immune system from things like HIV/AIDS, leukemia or certain medicines
If you have symptoms of cellulitis, see your doctor right away. Your doctor may be able to diagnose cellulitis with a simple physical exam. They may also take a blood or skin sample to find out what type of bacteria is causing the infection.
What Are the Medicines to Treat Cellulitis?

Your doctor can prescribe antibiotics to treat cellulitis. Most of the time, you can take these antibiotics as pills. If you have a severe infection, you may need to get intravenous (IV) antibiotics through a vein. In rare cases, you may need surgery to treat a severe infection.
Untreated cellulitis can cause serious health problems, including infections in your blood, bones and heart. It can even be life-threatening. That’s why it’s so important to get treatment from your doctor at the first sign of a cellulitis infection.
Sometimes cellulitis comes back after treatment, so you may need to take antibiotics again. Your doctor may also prescribe preventive antibiotics if you have chronic recurrent cellulitis (cellulitis that keeps happening again and again).
How Can I Prevent Cellulitis?
Taking care of any wounds or breaks in your skin is the best way to prevent all skin infections, including cellulitis. Take these steps to protect your skin:
- Keep cuts and wounds clean and dry — thoroughly wash wounds with soap and water and then allow them to dry
- Cover wounds with fresh bandages at least once a day
- Apply a protective ointment like Vaseline or polysporin
- Avoid going in hot tubs, swimming pools or other bodies of water when you have an open wound or infection
If you have diabetes or problems with your blood circulation, take extra steps to prevent skin infections:
- Check your hands and feet for any injuries or signs of infection every day
- Keep your skin moisturized to prevent skin damage
- Regularly trim your fingernails and toenails
- Protect your hands and feet by wearing socks and gloves when needed
- Get treatment right away for any signs of infection
Remember, always see your doctor right away if a wound becomes painful — or if you notice redness, swelling or warmth spreading out around a wound. These are signs of a skin infection, and you need to get early treatment to protect your health.
Resource Links:
- “Cellulitis” via Mayo Clinic
- “Cellulitis” via Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- “Cellulitis” via Johns Hopkins Medicine